
- #FRAGMENT LIFECYCLE HOW TO#
- #FRAGMENT LIFECYCLE UPDATE#
- #FRAGMENT LIFECYCLE ANDROID#
- #FRAGMENT LIFECYCLE CODE#
- #FRAGMENT LIFECYCLE DOWNLOAD#
Started: Activity is visible to the user.Created: Activity is now completely initialized and ready to configure its UI.Initialized: Activity instance is created and its properties initialized.The figure above shows different states that activity goes through during its lifecycle: Not using these components correctly can result in the system killing the process while it’s doing important work. As the user navigates within the app, activities go through different lifecycle states.ĭevelopers must understand how different components impact the process’s lifetime.
#FRAGMENT LIFECYCLE ANDROID#
Every Android app has one or more activities. The most common app component is Activity. That type depends on the app components that are currently running and their current state. The importance hierarchy categorizes processes as different types. The Android OS uses an importance hierarchy to determine which processes to keep alive or to kill. When no app component is running and the OS needs to free memory to run other apps, it kills the process. The OS creates the process when any of the app components need to execute. In most cases, every app runs in its own Linux process. The Android operating system (OS) is a multi-user Linux system. Understanding the Role of the Lifecycle in Apps
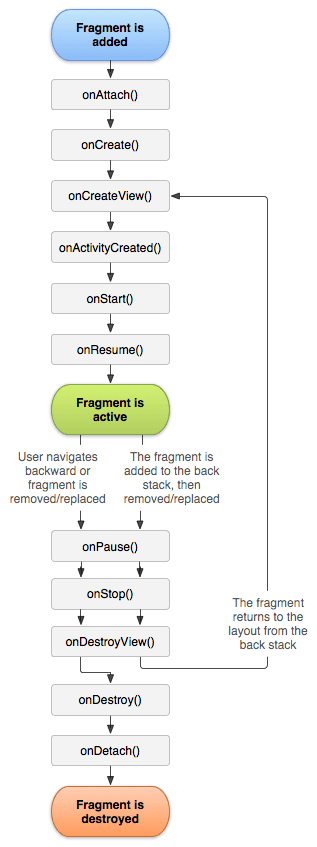
You’ll move between them as you learn about activity and fragment lifecycle. The most important packages are activities and fragments. :]Īs you can see, a lot is already prepared for you. In this tutorial, you won’t implement that logic, but you can pretend that it exists. Tap Share to open a dialog that asks you if you want to share your count.
#FRAGMENT LIFECYCLE UPDATE#
You can tap the cards or the plus and minus buttons to update the counters. Main screen: Allows you to count dogs of different sizes.Once the project opens, let it build and sync, and you’ll be ready to go! Open the starter project in Android Studio.
#FRAGMENT LIFECYCLE DOWNLOAD#
To start, download the materials by using the Download Materials button at the top or bottom of this tutorial.
#FRAGMENT LIFECYCLE HOW TO#

As the user navigates within the app, these components go through different states of the Android lifecycle. Imagine we have an activity that shows the device location on the screen.When it comes to building an Android app, activities and fragments are key components to building its user interface (UI). They are core to how Android worksĪnd your application must respect them.
#FRAGMENT LIFECYCLE CODE#
The framework code running in your process. Lifecycles are managed by the operating system or Most of the app components that are defined in the Android Framework have Into your Android project, see the instructions for declaring dependencies in the Package provides classes and interfaces that let you build lifecycle-awareĬomponents-which are components that can automatically adjust theirīehavior based on the current lifecycle state of an activity or fragment.
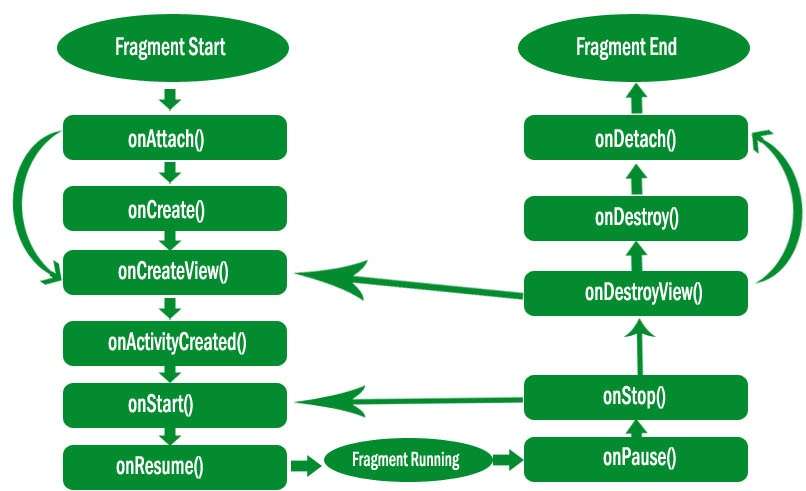
The lifecycle methods and into the components themselves. Lifecycle-aware components, you can move the code of dependent components out of Poor organization of the code and to the proliferation of errors. Lifecycle methods of activities and fragments. TheseĬomponents help you produce better-organized, and often lighter-weight code,Ī common pattern is to implement the actions of the dependent components in the Lifecycle status of another component, such as activities and fragments. Lifecycle-aware components perform actions in response to a change in the Handling Lifecycles with Lifecycle-Aware Components


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
